react 生命周期图
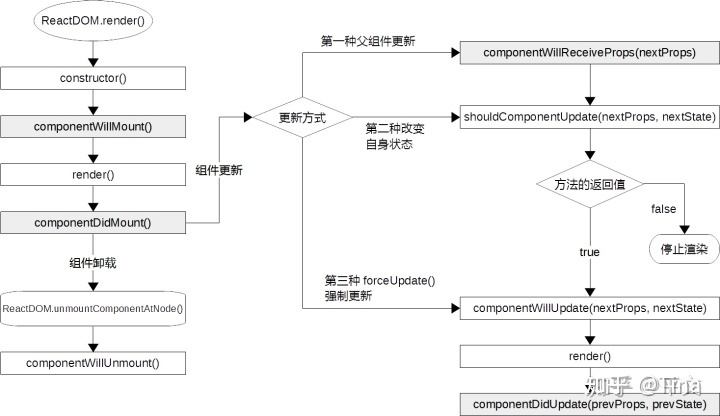
React 组件的生命周期
React 组件拥有丰富的生命周期钩子函数,遍布它的各个阶段。
其生命周期可被分为3 个阶段:
挂载(Mounting)、更新(Updating)和卸载(UnMounting)。
一、挂载阶段
这是 React 组件生命周期的第一个阶段,也可以称为组件出生阶段,这个阶段组件被初始化,获得初始的 props 并定义将会用到的 state。
此阶段结束时,组件及其子元素都会在 UI 中被渲染(DOM,UIview 等),我们还可以对渲染后的组件进行进一步的加工。
挂载阶段,组件会完成它的首次渲染,先执行初始化,再被挂载到真实的 DOM 中,其中依次调用的方法有 constructor()、componentWillMount()、render() 和componentDidMount()。除了 render(),其他三个方法都只会运行一次。
getDefaultPropos:只调用一次,实力之间共享引用。getInitialState:初始化每个实例特有的状态。componentWillMount:render 之前最后一次修改状态的机会。render:只能访问 this.props 和 this.state,只有一个顶层组件,不允许修改状态和 DOM 输出。componentDidMount:成功 render 并渲染完成真实 DOM 后触发,可以修改 DOM。
1. constructor()
在生命周期中,类的构造函数 constructor() 会率先被执行,用于初始化组件的状态、接收外部传递进来的数据、绑定成员方法的 this 指向等工作。(只执行一次)
2. componentWillMount()
componentWillMount():会运行在 render() 之前,它是渲染之前的回调函数。不过,由于在这个方法中执行的任务都能提前到 constructor() 中,因此实际项目中很少会用到它。(只执行一次)
3. render()
render():是在定义组件时必须声明的方法,它是一个无副作用的纯函数,可根据组件的 props和 state 得到一个React 元素、null 或 false 等返回值,并且在 render() 方法中不能调用改变组件状态的 this.setState() 方法。注意,将元素渲染到页面 DOM 中的工作都由 React 负责,而不是 render() 方法。
4. componentDidMount()
componentDidMount():会运行在 render() 之后,它是渲染之后的回调函数。此时组件已被挂载到页面中,可以执行 DOM 相关的操作,例如异步读取服务器中的数据并填充到组件中、调用 jQuery 代码等。(只执行一次)
二、更新阶段
引起组件更新(即重新渲染)的方式有三种:
第一种:由父组件向下传递 props(即调用父组件的 render() 方法)引起的更新,依次会调用五个方法:
componentWillReceiveProps()shouldComponentUpdate()componentWillUpdate()render()componentDidUpdate()
第二种:通过改变自身 state(即调用this.setState()方法)引起的更新,会忽略componentWillReceiveProps() 方法,只执行四个回调函数。
第三种:通过组件的 forceUpdate() 方法强制更新,只有后三个回调函数会被执行。
1. componentWillReceiveProps()
componentWillReceiveProps():常用于执行 props 更新后的逻辑,只有第一种更新方式才会调用它。
该方法能接收一个名为 nextProps 的参数,表示父组件传递进来的新的props。
当需要通过 this.setState() 方法将 nextProps 中的数据同步到内部状态时,要先比较 nextProps 和this.props 中的值是否相同,再决定是否执行同步。
由于在 componentWillReceiveProps() 中能调用 this.setState() 方法,因此为了避免进入一个死循环,在调用 this.setState() 方法更新组件时就不会触发它。
2. shouldComponentUpdate()
shouldComponentUpdate():用于决定是否继续组件的更新。
它能接收2个参数:nextProps 和 nextState,分别表示新的 props 和 state。
通过比较 nextProps、nextState 和组件当前的 this.props、this.state 能得出一个布尔类型的返回结果。
当返回结果为 false 时,组件会停止更新,后续的 componentWillUpdate()、render() 和 componentDidUpdate() 也不会被执行。
将这个方法使用恰当的话,能减少冗余的渲染,优化组件的性能。
3. componentWillUpdate()
componentWillUpdate():运行在 render() 之前,接收2个参数,提供更新之后的 props 和 state。
4. componentDidUpdate()
componentDidUpdate():运行在 render() 之后,接收2个参数,提供更新之前的 props 和 state。
注意,在 componentWillUpdate() 中,不能调用 this.setState() 方法,以免发生不必要的死循环。
三、卸载阶段
当组件在从 DOM 中被卸载之前,会触发一个无参数的 componentWillUnmount() 方法。在该方法内适合做些清理的工作,例如清除定时器、移除多余的DOM元素等。
componentWillUnmount()
过时和新增的回调方法
1、过时
从 React v16.3 开始,有 3 个生命周期方法被标记为过时:componentWillMount()、componentWillReceiveProps() 和 componentWillUpdate()。
目前它们仍然有效,但不建议在新代码中使用,官方为它们新增了一个以“UNSAFE_”作为前缀的别名。
2、新增
React v16 新增了两个生命周期方法,如下所列。
【1】static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState)
静态方法 getDerivedStateFromProps() 用来替代 componentWillReceiveProps()。
它在 render() 方法之前触发,包含两个参数:nextProps 和 prevState,分别表示新的 props 和旧的 state。
如果返回一个对象,那么更新 state;如果返回 null,那么就不更新 state。
【2】getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState)
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() 方法用来替代componentWillUpdate()。
它在最近一次渲染输出(即更新DOM)之前触发,包含两个参数:prevProps 和 prevState,分别表示旧的 props和旧的 state,返回值会成为 componentDidUpdate() 的第三个参数。